Article type:
Case Report
Article
title: Stroke
and poor therapeutic adherence in giant cell arteritis: a case report
Journal: Romanian Journal of Neurology
Year: 2018
Authors: Jamir Pitton Rissardo, Ana Letícia Fornari
Caprara
E-mail: jamirrissardo@gmail.com
ABSTRACT
Giant cell arteritis
(GCA) is an inflammatory disease involving mainly the cranial arteries
branches. We present a case of an old male with right hemiparesis that was
admitted to our hospital. The subject's daughter stated that the patient had
gone to another clinic 3 months ago because he experienced anorexia and temple
headache. A temporal artery biopsy proved GCA. Prednisone was started. Within
one month, the prednisone-dose was 40mg/day. The patient was asymptomatic, but
the prednisone-dose was maintained because he had elevated inflammatory
markers. On admission, the subject had right limb weakness and global-aphasia
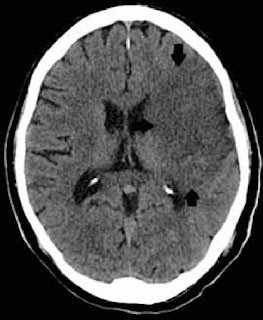
with six hours of onset. Twelve hours after admission, the patient developed a
seizure, and a CT-scan showed a hypodense area in the territory of the left
middle cerebral artery. Upon further questioning, the subject's family admitted
that he reduced the dose of prednisone of 40mg/day to 10-20mg/day without any
medical advice 2-weeks after the stroke.
Keywords: Stroke, giant cell arteritis, steroids
Full text
available at:
Citation
Rissardo JP, Caprara AL. Stroke and poor therapeutic adherence in giant cell arteritis: a case report. Rom J Neurol 2018;17:217-219