Myotonic disorders!
“after a fright, or in an unexpected joyous movement, this convulsive constriction occurs in all limbs…the victim can not stand upright”
Prussian physician Asmus Julius Thomas Thomsen (1815–1896) 2) Definition
“difficulty in relaxation of a muscle after maximum voluntary contraction”
It can be specifically
- aggravated by conditions
- affecting regions of the body
- triggered
“important in history due to role of chloride channel in muscle excitation”
- 1880s, Marshall County
- CLCN1 gene
4) Classification of myotonic disorders
Waxing & wanning of both amplitude & frequency
Potentials
- repetitive discharges
- 2 types: biphasic (<5ms) and positive waves (5-20ms)
7) Electrical myotonia differential
“tries to open his eyes after having squeezed them tight”
- persist 1-2 minutes
- recruit additional muscles: frontalis
4) Classification of myotonic disorders
6) Dive-bomber
“High frequency discharges in EMG that vary in amplitude & frequency, waxing & waning continuously with firing frequencies ranging from 150/second down to 20/second and producing a sound that has been referred to as a dive bomber sound
*turn sound on
7) Electrical myotonia differential
9) Tongue myotonia
10) Handgrip myotonia
“make a fist and then fully open the hand”
- open of the fist require other hand
11) Handgrip myotonia
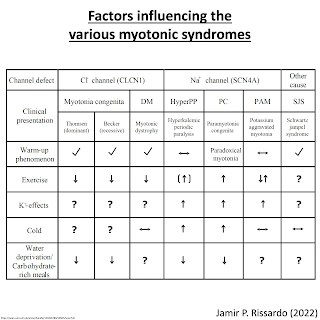
12) Warm-up phenomenon vs paramyotonia
14) Tented Mouth
“triangular appearance of the oral aperture with the apex in the midpoint of the upper vermilion and the lower vermilion forming the base”
- congenital myotonic dystrophy
17) Smooth muscle myotonia
18) Myotonic dystrophies
DM 1
- CTG trinucleotide repeat on DMPK gene
- most common myotonic disorder
DM 2
- CCTG tetranucleotide repeat on CNBP gene
- rare disorder
24) Paramyotonia congenita
Paradoxical myotonia
1st signs of stiffness as prolonged eye closure, after
- crying
- sleep near a fan
- washing face w/ cold water
25) Hyperkalemic periodic paralysis
“early childhood w/ episodes of periodic weakness”
- attacks in the morning & fasting
- 3 variants: HyperKPP w/o myotonia; w/ myotonia; w/ paramyotnia
26) Schwartz-Jampel syndrome (chondrodystrophic myotonia)
"prominent and diffuse myotonia that is present at birth"