Blood-brain barrier & circumventricular organs
German physician Paul Ehrlich (1854-1915)
4) BBB is formed by “BBB”
Binding tight junctions
Basement membrane
Base-foot astrocyte
6) Pass
Have 3 types of transport in the body PTT
- Paracellular
- Transcellular
- Transcytotic-vesicular
7) In the BBB
- No paracellular due to tight junctions
- poor transcellular and transcytotic-vesicular
You have guards in the CNS – P-glycoproteins
- take lipid soluble substances out the brain
- energy-dependent transport
8) What does not pass BBB?
BIG guys – plasma proteins & substances attached to them
HORNY guys – highly charged
TOXIC guys – even if small
What does pass BBB?
BABY molecules – H2O, O2, CO2
- But, H+ no, He is a Horny guy
SWETTY guys – glucose & aminoacids (carrier mediated)
9) BBB vs BCF difference
Where is the tight junction is the ≠
BBB – Blood (endothelial)
vs
BCB – Choroidal (choroidal epithelial cells)
10) Types of cerebral edema
COVI: Cytotoxic, Osmotic, Vasogenic, Interstitial
- vasogenic is considered the MC
- doesn’t have a clear mechanism, may be a combination of mechanisms
Types
Intracellular – cytotoxic & osmotic
Extracellular – vasogenic
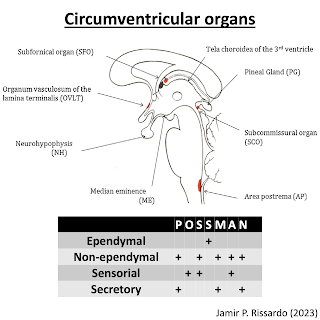
11) Circumventricular organs
- circumventricular organs are specialized areas of CNS where BBB is modified or broken
- all of them are surrounded by 3rd & 4th ventricles
- ependymal cells proximal to ventricular areas are modified and their name are tanycyte
13) Tanycyte
- line the floor of the 3rd ventricle
- conduit between CSF and blood
15) "POSSMAN"
17) OVLT (organ vasculosum of lamina terminalis)
Receptors: ATII; IL-1; osmoreceptors
It is where the location of the anterior neuropore. If not closes, you will have anencephaly.18) Subforniceal organ
Receptors: ATII
Thirsty & fluid balance19) Subcommissural organ
Reissner’s fibers
- glycoproteins that keep ventricular system patent
- deficiency causes stenosis of spinal canal20) Median eminence of hypothalamus
Control anterior hypophysis21) Area postrema
CTZ
Dorsal vagal triangle22) Neurohypophysis
Secrete hormones